The term "metal fabrication" is used to describe any procedure that alters metal in some way, such as cutting, bending, or assembly. Steel is one of the most widely used metals for fabrications, though many others can be used. Steel's high tensile strength is just one of many useful characteristics.
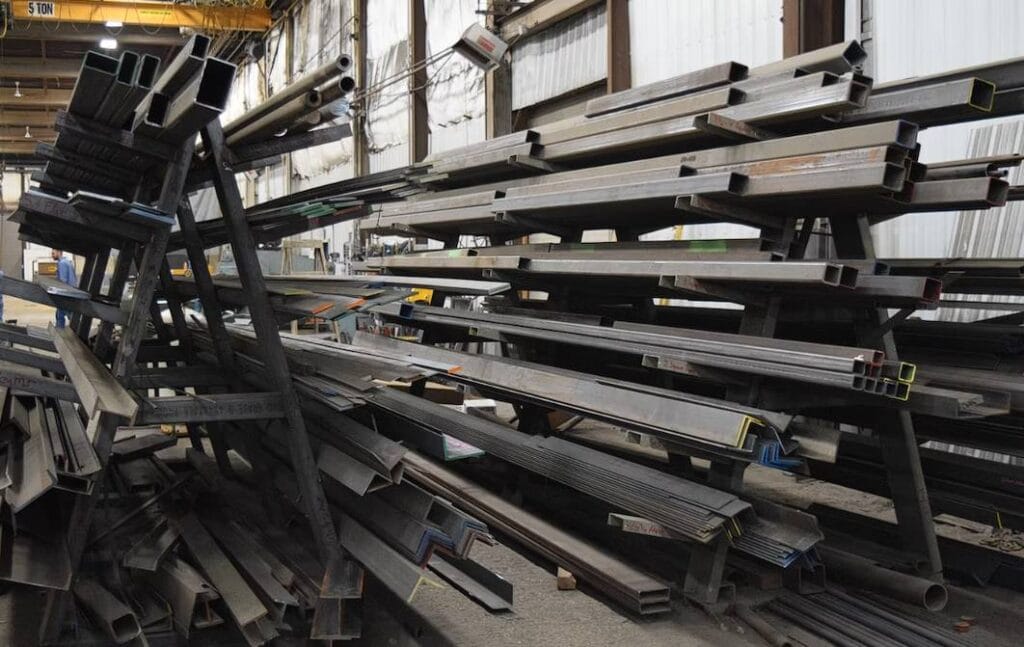
Steel can be precisely fabricated to meet exacting standards, and some varieties, like stainless steel, are highly resistant to corrosion, even rust. Steel can be purchased in many shapes, including flat sheets, rods, plates, tubes, and I-beams.
In the steel fabrication industry, jobs fall into light and heavy categories. Differences and similarities between heavy and light steel fabrication are outlined below.
What Is Heavy Metal Fabrication?
"heavy metal fabrication" describes the industrial practice of producing objects from more substantial metal sheets. These materials' density, strength, and longevity make them indispensable in many fields. Fabrication of heavy metals is widely used in fields like building, shipping, mining, and infrastructure building.
This specialised fabrication method is used to create massive structures, equipment, and machinery that can withstand intense pressure and severe weather. Heavy metal fabrication uses thick and strong metals to produce long-lasting products that can withstand the rigours of an industrial environment.

Fabrication Processes
Working with bigger and bulkier raw materials necessitates robust manufacturing procedures when working with heavy metals. Specialised machinery, such as plasma cutters and large rollers, are used to process these materials efficiently. Large rollers make it easier to form the metal into the ideal shapes and structures after cutting precisely with plasma cutters.
Welds in heavy metal fabrication are also subjected to stricter quality controls. The importance of these massive undertakings necessitates extensive testing to guarantee they will perform as expected under stress and last as long as planned. Because of how crucial these manufactured structures are to last, strict quality control measures must be implemented whenever heavy metal is used in the building process.
Raw Materials
Steel and stainless steel are indispensable in the production of heavy metals. Beams, plates, and pipes are all examples of this material that play an important role in manufacturing. The use of sheet metal in heavy metal fabrication also increases the variety of materials available for constructing long-lasting metal structures.
Location Of Fabrication
Fabrication of heavy metals produces massive, cumbersome byproducts. As a result, it makes sense to complete the steps where the project will be built. This entails bringing all necessary materials to the work site.
Problems arise when trying to transport tools to the site. The first issue is getting the large and specific tools to the construction site. Second, there are precautions that must be taken by the workers when operating the machinery. And finally, controlling the equipment's dust, fumes, and trash throughout the project's duration.
Final Products
The fabrication of heavy metals focuses on massive and oversized products. Large-scale projects like farm machinery and military hardware are ideal candidates for this production method. Industries can effectively produce tough, resilient machinery that can handle these fields' rigours by using heavy metal fabrication techniques.
What Is Light Metal Fabrication?
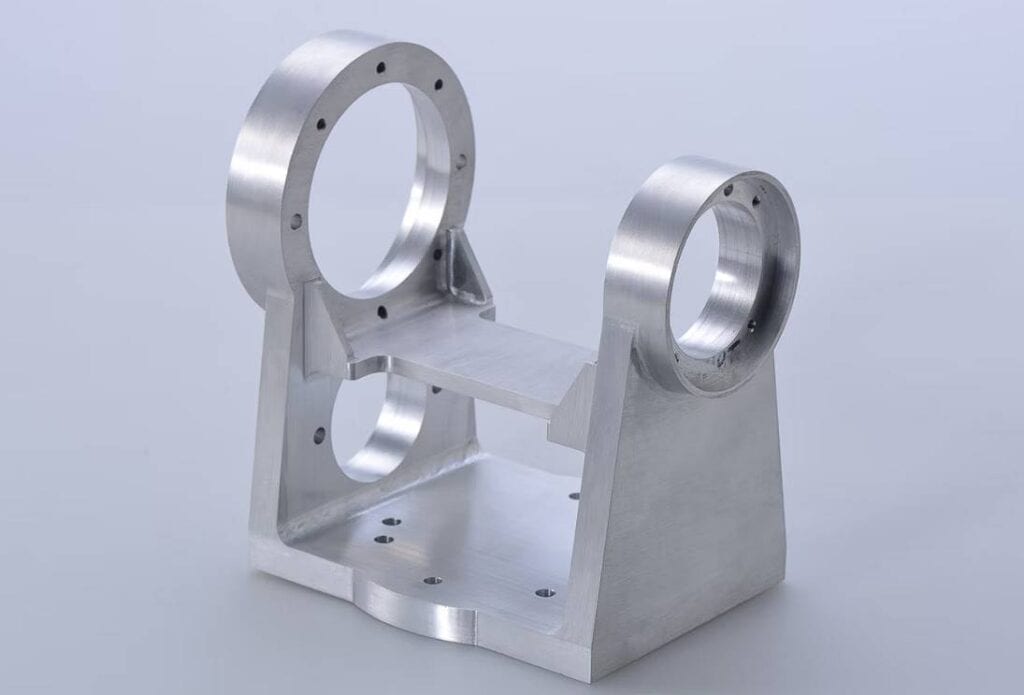
Thinner and lighter metals are the focus of light metal fabrications. These metals are chosen due to their adaptability, malleability, and corrosion resistance. Light metal fabrications are widely used in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and consumer goods industries. Precision, intricate designs, and the production of lightweight, durable components are prioritised during this stage of fabrication.
Light metals allow for the creation of products that strike a fine balance between durability and portability, making them ideal for use in sectors where these factors are of paramount importance. Light metal fabrications truly shine when it comes to meeting the complex and demanding needs of today's industries.
Fabrication Processes
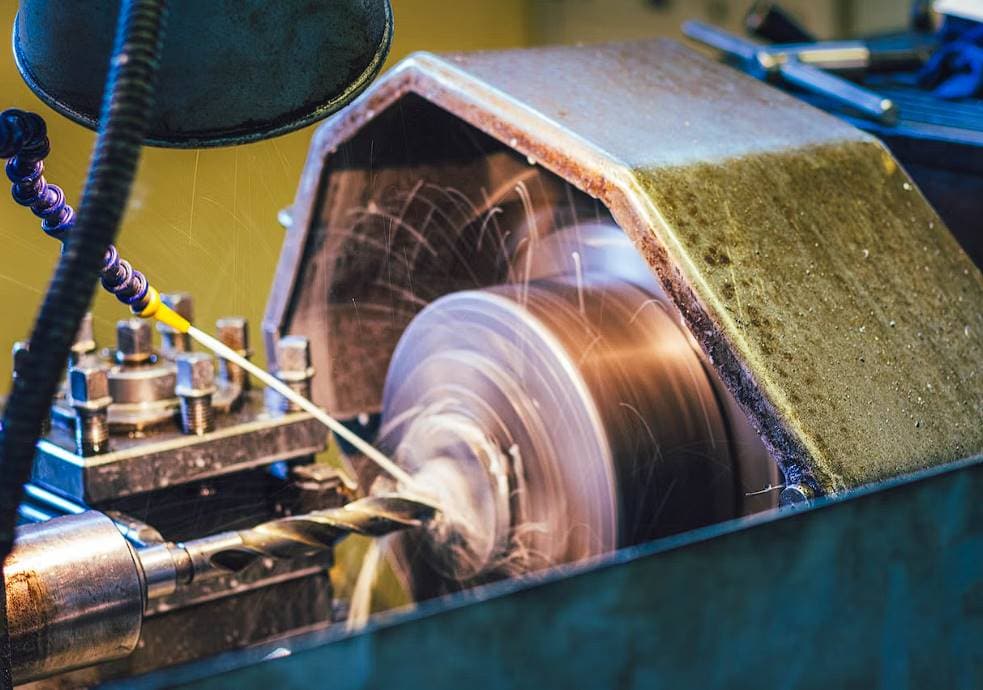
Light metal fabrication benefits greatly from the use of thinner and lighter materials. These materials are less hassle and can be modified with tools like mills and lathes. Fabrication is streamlined because of the adaptability and light weight of these materials.
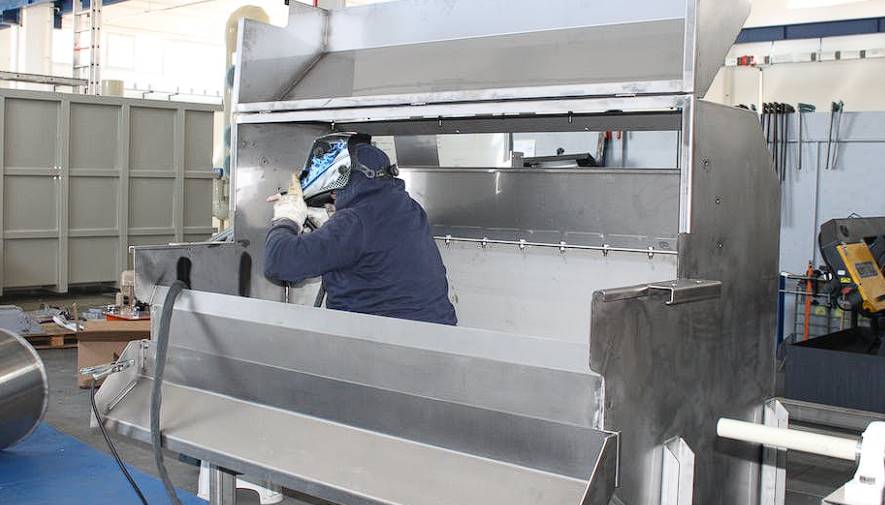
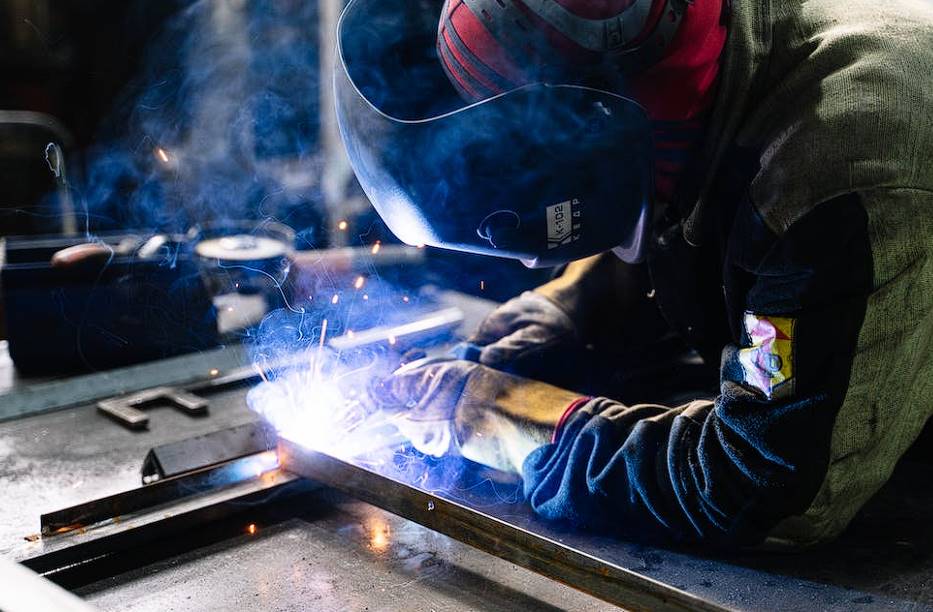
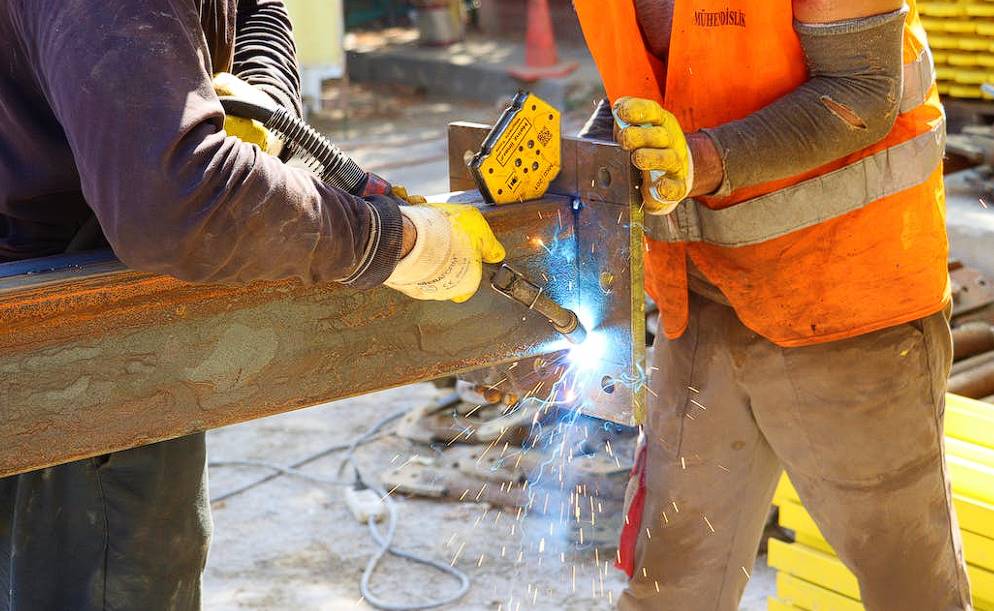
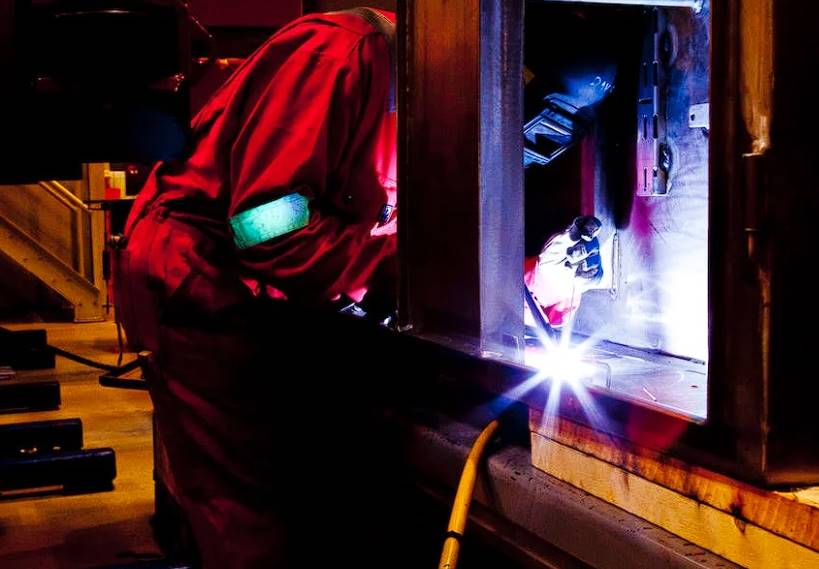
With one exception, welding techniques are used in heavy and light steel fabrication. When working with thicker and more substantial metals, resistance welding is less effective than it is when working with lighter gauge metals. Gas metal arc welding and arc welding (GMAW) are two other common welding techniques used in heavy metal fabrication, both of which produce strong, long-lasting welds.
Raw Materials
Aluminium sheet metal is widely used as a primary material for lightweight fabrication. It is highly versatile due to its low weight and high resistance to corrosion. However, extruded aluminium is used exclusively in lightweight metal fabrication due to its increased strength and adaptability.
Aluminium is not the only metal used in light fabrication; brass, copper, and stainless steel are also frequently used. These materials strike a nice balance between sturdiness and portability, making them ideal for use in sectors as varied as electronics, aerospace, and consumer goods.
Location Of Fabrication
Light metal fabrication projects have the benefit of being easily transportable. Because of their reduced bulk, these endeavours can be relocated with relative ease. In contrast to the time and money spent on heavy fabrication projects, which must be done on-site, light fabrication projects can easily be brought to fabrication shops. The execution of light metal fabrication projects is made more convenient and approachable as a result of this adaptability. Light metal fabrication presents fewer logistical challenges for manufacturers and fabricators, making it easier to manage and complete projects in a timely manner.
Final Products
The production of metal goods with a thickness of less than one inch is included in the scope of the term "light metal fabrication." It focuses on the production of smaller components, such as brackets and other intricate metal parts, as its primary line of business. This process makes it possible to precisely fabricate metal items that are small and intricate, making them useful in a wide variety of industries and applications.
Comparison Of The Fabrication Of Heavy And Light Metals
Both heavy and light metals can be fabricated, but they have different purposes. Despite the similarities in the use of metals, the two techniques are very different. This will examine and contrast the processes of fabricating heavy metals and fabricating light metals, focusing on the key differences between them.
Professionals and amateurs alike can benefit from knowing the key differences between these two metal fabrication techniques so they can select the best method suited to their projects.
Expertise And Experience In Manufacturing
Heavy steel production is more complicated than its lighter counterpart and requires specialised knowledge from the producer. Heavy steel projects necessitate specialised machinery and methods and trained workers who are familiar with working with massive materials. OEMs must find a manufacturer with the resources to complete light and heavy steel fabrication projects safely and efficiently.
Workflow And Facilities
Large and heavy fabrication is only possible to move around the shop with cranes or other specialised machinery. It is common practice to bring the processing steps there to reduce the amount of time and effort spent transporting the heavy fabrication.
On the other hand, light steel fabrications are easier to move around as needed during the various stages of production. Light fabrication projects do not necessitate nearly as much space and specialised facilities as heavy fabrication projects because of the size and scope of the cranes and other equipment needed for the former.
Structural Differences
The structural characteristics are the most obvious difference between heavy and light metal fabrication. Fabricating with heavy metal is about making strong, long-lasting structures that can take a beating from both human use and the elements. On the other hand, light metal fabrication focuses on making lightweight structures that value adaptability and manoeuvrability over brute strength.
While heavy metals in fabrication guarantee exceptional strength, the use of lighter metals allows for greater flexibility in situations where speed and dexterity are essential. These differences significantly impact the performance and applicability of fabricated structures across sectors and projects. They should be taken into account when picking between heavy metal fabrication and light metal fabrication.
Size And Final Products
The oil and gas industry, the military, the construction industry, and even the aerospace industry all make extensive use of light and heavy fabrications. Fabrications made from heavy steel are typically much more substantial and expansive than those made from light steel. Products like hand tools, grating, original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts, and modest structures fall under "light steel fabrications."
Heavy steel fabrications, on the other hand, involve products like propellers and mining equipment, where sturdiness and longevity are of the utmost importance. When industries have a firm grasp on the differences between light and heavy fabrications, they can select the most suitable fabrication strategy in accordance with their unique needs, thereby maximising performance and reliability.
Strength And Durability
Its primary advantages in the field of heavy metal fabrication lie in the areas of strength and durability. Using thick and heavy metals ensures that the resulting structures will be strong enough to withstand intense pressure and keep going no matter what nature throws at them. While light metal fabrication isn't as sturdy as its heavy counterpart, it does have benefits like portability and lower material costs.
Metals with lower specific gravities can be used to build lighter, more easily transported and set up structures. This makes lightweight metal fabrication a good option for uses where portability and low mass are highly valued without sacrificing functionality or performance.

Fabrication Techniques
Steel construction projects use various fabrication techniques to shape raw materials into the final product, including cutting, bending, and joining. Some of the most typical approaches to fabrication are described below.
Forming
Rolling and bending are common ways to form steel, which is needed for many light and heavy steel fabrication projects. Section, tube, press, and plate bending are just some methods that can be used to bend the structure into the desired shape. While a press is commonly used for forming the metal in light fabrications, the metal thickness could be more effective when working with heavy fabrications.
Welding
Welding is an integral part of any substantial fabrication endeavour. The size of the welds is a common criterion for classifying steel fabrications as either light or heavy. In contrast to the structural-single-pass welds used in light fabrication, heavy fabrication often requires a large prep area and full penetration/UT welding. All of this is carried out through either automated or traditional methods of welding, whichever the client prefers. Due to the increased metal thickness, heavy fabrications may also necessitate more extensive pre-heating and more frequent maintenance.
Cutting
For most fabrication jobs, the first step is to take a massive sheet of metal and cut it down to size. Metal can be cut into pieces using various specialised tools and processes, including laser, gas, saw, waterjet, and plasma cutting. Cutting is used in light, and heavy steel fabrication, but different cutting processes are more appropriate for each. For instance, cutting methods like notching and shearing are ideal for lightweight fabrications due to the typically thinner steel used in such projects.
Punching And Drilling
These procedures are essential in getting the fabrication ready to be bolted together. These methods are used in both lightweight and substantial manufacturing. A turret punch is ideal for less intensive fabrications, while computer numerically controlled (CNC) punch presses are frequently used for both light and heavy steel projects.
Blasting Or Painting
Many projects are sandblasted or painted after the fabrication and welding are finished. Just welding, blasting, and painting can be done in a robotic cell. Heavy steel fabrications are more likely to require blasting and painting than their lighter counterparts because of the extreme conditions to which they will be subjected in the field.
Conclusion
Heavy metal fabrication involves the industrial process of producing objects from larger metal sheets, such as steel, which is widely used in fields like building, shipping, mining, and infrastructure building. This method is essential for creating massive structures, equipment, and machinery that can withstand intense pressure and severe weather. Heavy metal fabrication uses thick and strong metals to produce long-lasting products that can withstand the rigours of an industrial environment.
Fabrication processes for heavy metals require robust manufacturing procedures, such as using specialized machinery like plasma cutters and large rollers. These materials are subjected to stricter quality controls, ensuring they perform as expected under stress and last as long as planned. The use of sheet metal in heavy metal fabrication increases the variety of materials available for constructing long-lasting metal structures.
Light metal fabrication focuses on thinner and lighter metals due to their adaptability, malleability, and corrosion resistance. These materials are widely used in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and consumer goods industries. They allow for the creation of products that strike a fine balance between durability and portability, making them ideal for sectors where these factors are of paramount importance.
Light metal fabrication projects are easier to transport due to their reduced bulk, making them more convenient and approachable. This makes it easier to manage and complete projects in a timely manner.
Light metal fabrication also focuses on producing smaller components, such as brackets and other intricate metal parts, as its primary line of business. This process allows for precise fabrication of metal items that are small and intricate, making them useful in a wide variety of industries and applications.
In conclusion, both heavy and light metal fabrication have different purposes and processes. Heavy steel production requires specialized knowledge and experience from the producer, while light metal fabrication requires specialized machinery and facilities. Understanding the key differences between these two metal fabrication techniques can help professionals and amateurs select the best method suited to their projects. Heavy and light steel fabrications have distinct structural characteristics, with heavy metal fabrication focusing on creating strong, long-lasting structures that can withstand harsh conditions. Light metal fabrication, on the other hand, focuses on lightweight structures that value adaptability and manoeuvrability over brute strength. These differences significantly impact the performance and applicability of fabricated structures across sectors and projects.
The oil and gas, military, construction, and aerospace industries all use heavy and light steel fabrications. Heavy steel fabrications involve products like propellers and mining equipment, while light metal fabrications are more substantial and expansive.
Strength and durability are primary advantages in heavy metal fabrication. Heavy fabrications require a large prep area and full penetration/UT welding, while light metal fabrications have portability and lower material costs. Cutting is a common process in both light and heavy steel fabrications, with different cutting methods suitable for each.
Punching and drilling are essential for bolting together the fabrication, with turret punches being ideal for less intensive projects and computer numerically controlled (CNC) punch presses for both light and heavy steel projects. Sandblasting or painting is common after fabrication and welding, with heavy steel fabrications more likely to require blasting and painting due to the extreme conditions they face in the field. Understanding the differences between light and heavy fabrications allows industries to select the most suitable strategy for their unique needs, maximizing performance and reliability.
Content Summary
- Metal fabrication involves cutting, bending, and assembly of metal materials.
- Steel is commonly used for fabrications due to its high tensile strength.
- Stainless steel is resistant to corrosion, including rust.
- Steel comes in various shapes, such as sheets, rods, plates, tubes, and I-beams.
- Metal fabrication can be categorized into heavy and light.
- Heavy metal fabrication is used in building, shipping, mining, and infrastructure.
- Heavy metal fabrication creates structures that can withstand intense pressure and severe weather.
- Specialized machinery like plasma cutters and large rollers are used in heavy metal fabrication.
- Welds in heavy metal fabrication undergo strict quality control.
- Steel and stainless steel are common raw materials in heavy metal fabrication.
- Heavy metal fabrication is often done on-site due to the bulkiness of the materials.
- Heavy metal fabrication is used in large-scale projects like farm machinery and military hardware.
- Light metal fabrication involves thinner and lighter metals.
- Light metal fabrication is used in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and consumer goods industries.
- Light metal fabrication prioritizes precision, intricate designs, and lightweight, durable components.
- Aluminium sheet metal is widely used in light metal fabrication due to its versatility and corrosion resistance.
- Brass, copper, and stainless steel are also used in light metal fabrication.
- Light metal fabrication projects are easily transportable.
- Light metal fabrication can be done in fabrication shops, making it more convenient.
- Light metal fabrication focuses on producing smaller components like brackets and intricate metal parts.
- Heavy metal fabrication requires specialized knowledge and machinery.
- Heavy steel fabrication projects need space and specialized facilities.
- Heavy metal fabrication produces strong, long-lasting structures.
- Light metal fabrication emphasizes adaptability and maneuverability.
- Heavy steel fabrications are generally larger and more substantial than light steel fabrications.
- Light metal fabrication offers portability and lower material costs.
- Forming, rolling, and bending are common techniques used in metal fabrication.
- Welding is a critical part of both heavy and light metal fabrication.
- Cutting is a necessary step in metal fabrication using various tools and processes.
- Punching and drilling are essential in preparing the fabrication for assembly.
- Blasting and painting are often done after welding for finishing heavy metal fabrications.
- Light metal fabrication uses notching and shearing cutting methods for thinner steel.
- Heavy metal fabrication may require more extensive pre-heating and maintenance for welding.
- Heavy metal fabrication uses large prep areas and full penetration welding techniques.
- Heavy metal fabrications are commonly used in the oil and gas, military, and construction industries.
- Light metal fabrication is commonly used in electronics, aerospace, and consumer goods.
- Heavy metal fabrications prioritize strength and durability.
- Light metal fabrications prioritize portability and low mass.
- Heavy metal fabrication is ideal for machinery and equipment that face rigorous conditions.
- Light metal fabrication is ideal for industries valuing precision and adaptability.
- Heavy metal fabrications often involve beams, propellers, and mining equipment.
- Light metal fabrications often involve brackets, hand tools, and consumer goods components.
- Heavy metal fabrication requires trained workers and specialized machinery.
- Light metal fabrication is more easily moved around during production.
- Heavy metal fabrication involves thicker and heavier materials.
- Light metal fabrication involves thinner and lighter materials.
- Heavy metal fabrication uses welding techniques like full penetration/UT welding.
- Light metal fabrication uses welding techniques like structural-single-pass welds.
- Heavy metal fabrication is best suited for projects that require exceptional strength and durability.
- Light metal fabrication is best suited for projects that value precision and portability.
Frequently Asked Questions
While light metal fabrication offers advantages such as weight reduction and versatility, it may have limitations in strength and durability compared to heavy metal fabrication. It is essential to consider the specific requirements of the project when choosing between the two types of fabrication.
Heavy metal fabrications offer exceptional strength, durability, and longevity. They can withstand heavy loads, extreme temperatures, and corrosive environments.
Light metal fabrications involve working with metals like aluminium, titanium, and magnesium due to their lightweight nature and excellent strength-to-weight ratios.
The aerospace, automotive, electronics, and consumer goods industries extensively utilise light metal fabrications for various applications.
Heavy metal fabrications generally involve higher production costs due to the materials and specialised equipment required. However, the specific project requirements should guide the cost analysis.