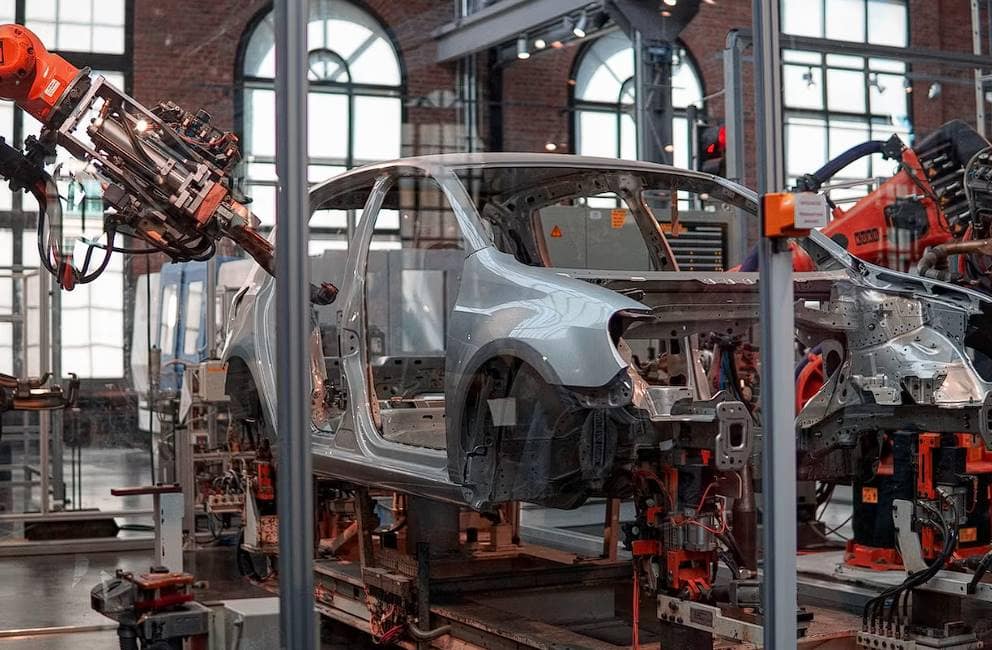
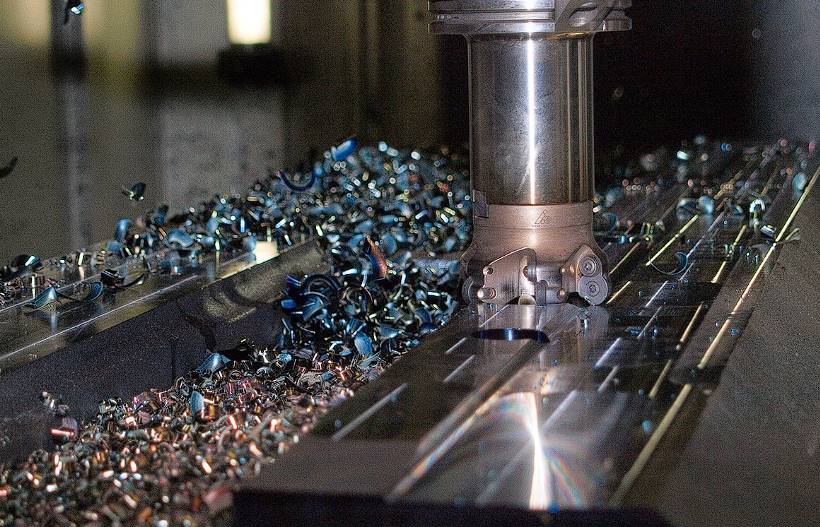
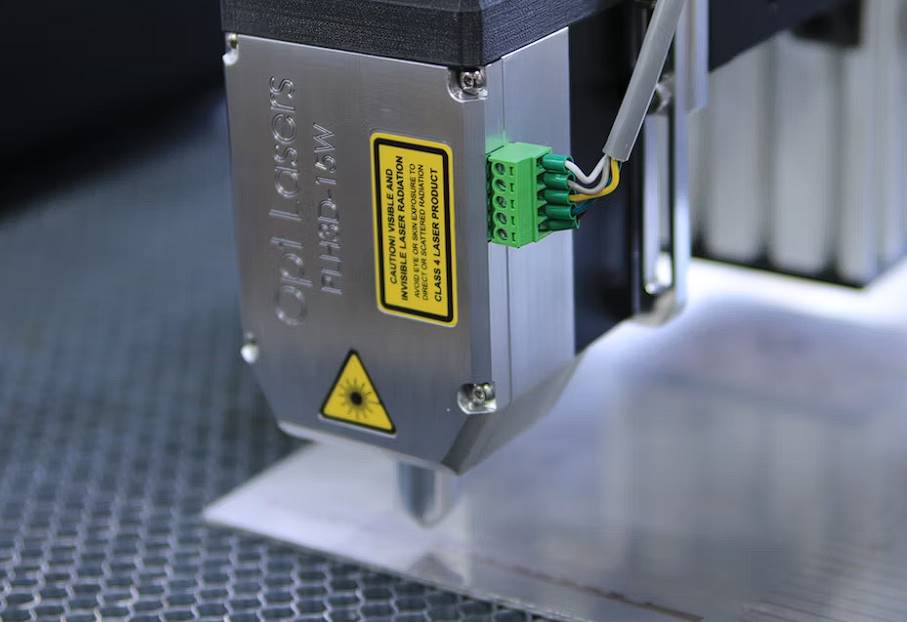
Amazing changes have occurred in manufacturing as a result of technical developments. For example, computer numerical control (CNC) machining has radically altered precision manufacturing. CNC machining is indispensable in producing high-precision parts for industries as diverse as aerospace, automotive, medicine, and electronics.
What Exactly Is Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machining?
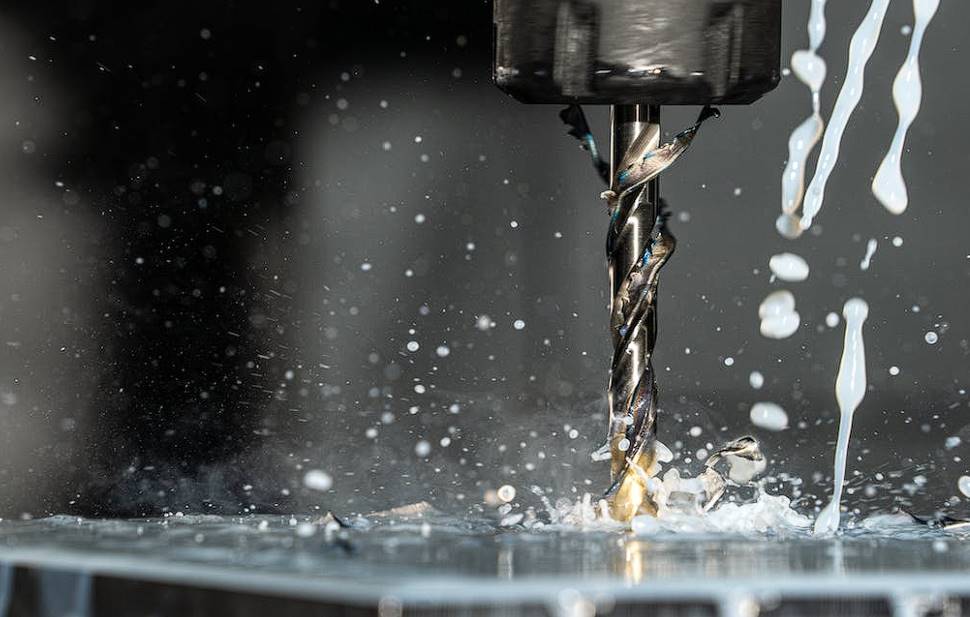
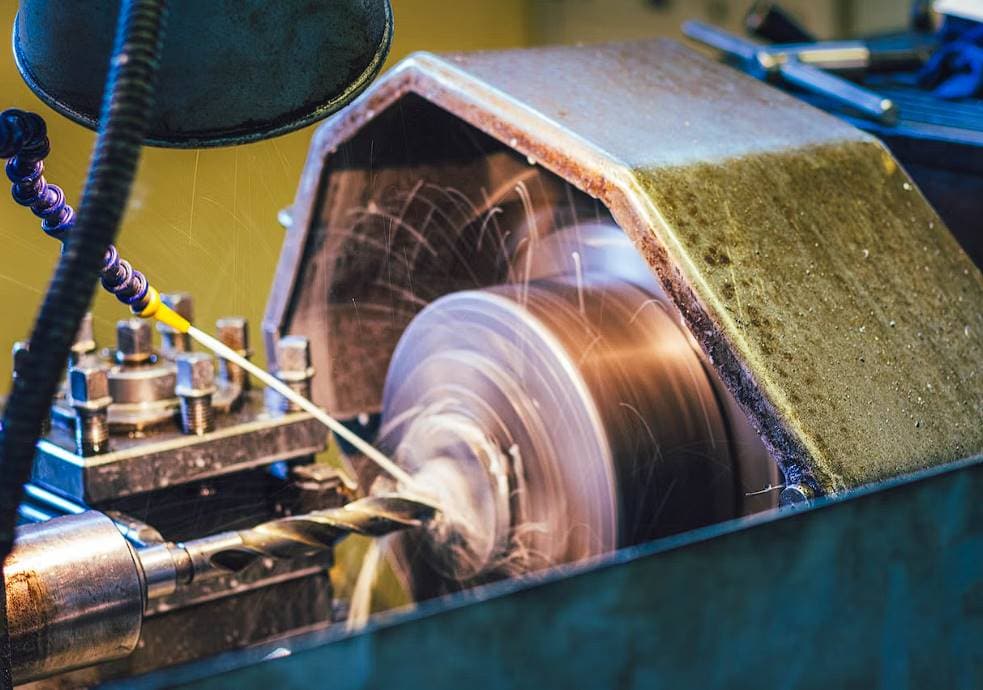
Subtractive manufacturing techniques, like CNC machining, involve removing rather than adding material throughout the making process. CNC machining employs a block of material (called a blank) and fast-moving cutters to quickly carve away excess material, resulting in the final item.
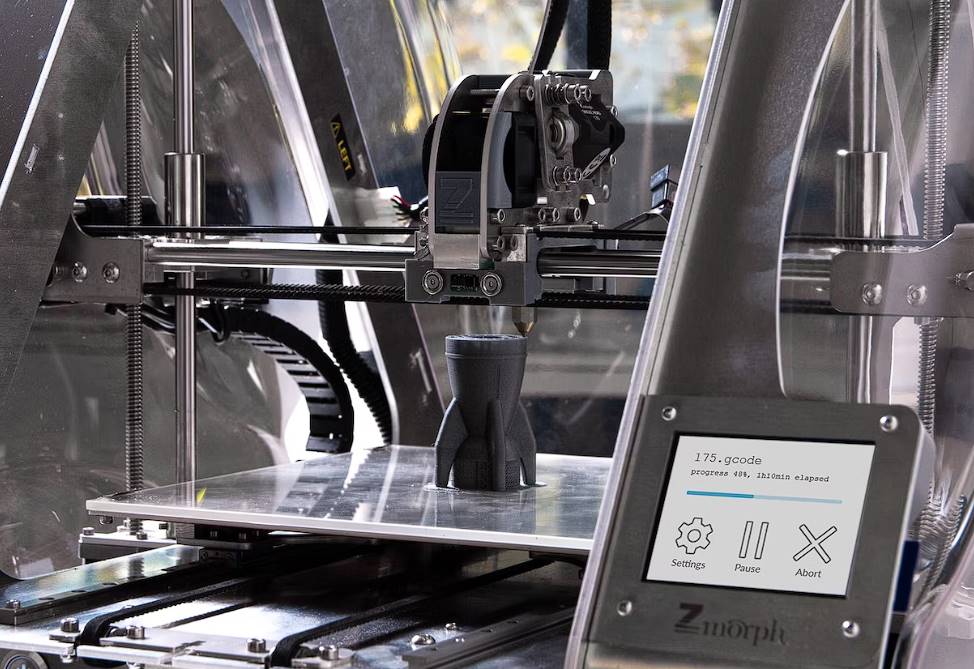
This makes it opposed to additive manufacturing, in which a three-dimensional object is manufactured by adding layers of material using a 3D printer.
CNC machining is also a form of metal manufacture in which the CNC machinery is controlled using computer code.
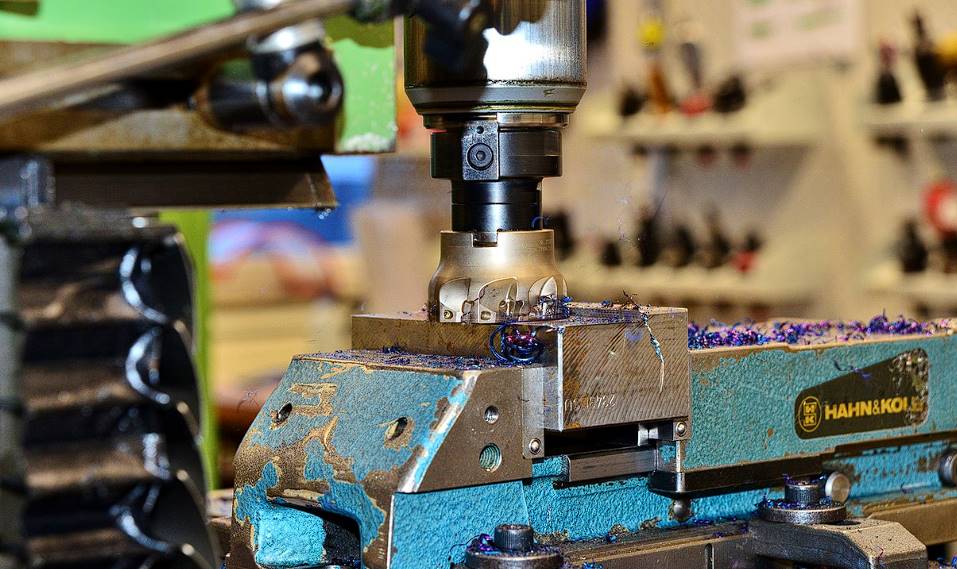

How Does CNC Work?
As we have just discussed, CNC machines are operated by a digital computer that monitors, automates, and controls the motion of an industrial machine. The computer is typically built into machinery in major factories, whereas it is attached externally in the case of amateurs.
The specific motions that this code can control are machine-specific. Let's have a peek into the guts of some of the most common CNC machines in use today:
Different Cnc Machines
Computer Numerically Controlled Milling Machines
CNC milling is a popular form of CNC machining due to its high precision and tight tolerances. CNC machines have pre-installed drilling and cutting equipment. Once materials are inserted inside the machine, the computer will direct the drilling and cutting tools to do the necessary operations.
Computer Numerically Controlled Lathe Machines
In contrast to CNC milling, which involves the movement of cutting tools to remove material, CNC turning involves the material being turned to remove it. In the middle of a CNC lathe machine is a lathe used to turn and move the material into place. This is yet another area of expertise for one of our reliable associates.
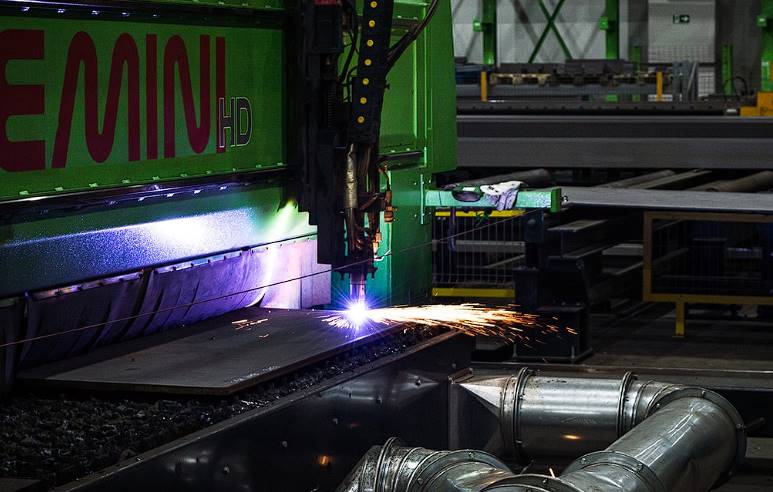
Computer Numerically Controlled Plasma-Cutting Machines
CNC plasma cutting machines, like CNC milling machines, are used to cut various materials. Their plasma torch can reach temperatures of up to 50,000 degrees Fahrenheit and cut through strong materials like metal, distinguishing them from milling machines.
Computer Numerically Controlled laser-Cutting Machines
Laser-cutting CNC machines are not to be mistaken with plasma-cutting CNC machines; both are geared for cutting through strong materials, although the former employs a laser beam rather than a plasma flame. These lasers can sometimes achieve greater cutting precision than plasma torches, although they are less powerful.
Computer Numerically Controlled Electric Discharge Machines
CNC electric discharge Spark CNC machines are a subset of computer numerical control machines (CNC machines) that use electrical sparks to shape materials. To reshape a portion, materials are inserted between an upper and lower electrode, and the computer then controls the amount of electrical discharge between them.
Equipment And Components Of Cnc Machining
The variety of machining processes is only the tip of the iceberg. For example, the CNC machining uses different software programmes, equipment, and machine tools to create the desired shape or design.
Software Categories for CNC Machining
CNC machining is used to produce an optimal, precise, and accurate version of a part or product developed in specialised software. Some of the programmes that are used are:
- CAM
- CAE
- CAD
Cam Stands For "Computer-Aided Manufacturing."
Software refers to the programmes that extract technical data from a CAD model, drive the CNC machine, and manipulate the tools to manufacture a unique item. CNC machines can operate autonomously with the help of CAM software, which can also perform quality control checks on the final output.
CAE Stands For "Computer Aided Engineering."
Software refers to the computer programmes used by engineers in the planning, execution, and debugging of a project. Design, planning, simulation, diagnostics, manufacturing, and repair are just some engineering analysis applications that can benefit from CAE software's use as a supporting tool. FEA, CFD, and MDB CAE software are offered.
Some programmes now incorporate CAM, CAE, and CAD features into a single package. This integrated programme, sometimes referred to as CAM/CAE/CAD software, has made it possible, for instance, for a single programme to manage the entirety of the fabrication process, from design through analysis and manufacturing.
CAD Stands For "Computer-Aided Design."
Software is computer programmes used to design and create technical drawings, models, and renderings of parts and assemblies in two or three dimensions, along with any accompanying technical documentation and specifications. Typically, a CAM programme will take the designs and models generated in a CAD programme and utilise them to develop the necessary machine programme to manufacture the item via CNC machining. You can use CAD software to create a virtual prototype of a product, test its functionality without a physical model, analyse and verify the design of individual components, and share design data with factories and shops.
What Are The Benefits Of CNC Machines?
Improved Accuracy And High Precision
CNC machining's precision is a major advantage over hand-operated methods. Precision parts can be manufactured without the constant supervision of an experienced worker.
CNC milling eliminates the potential for human mistakes in part fabrication by following precise computer-generated programming. However, the CNC machine operator still has some say in production.
The operator significantly impacts the precision of the CNC milling process. The operator regulates the working environment and calibrates the cutting tools. They must also be able to tell whether the tooling is too worn to produce satisfactory results when touched with raw materials. However, the overall possibility of human error is diminished.
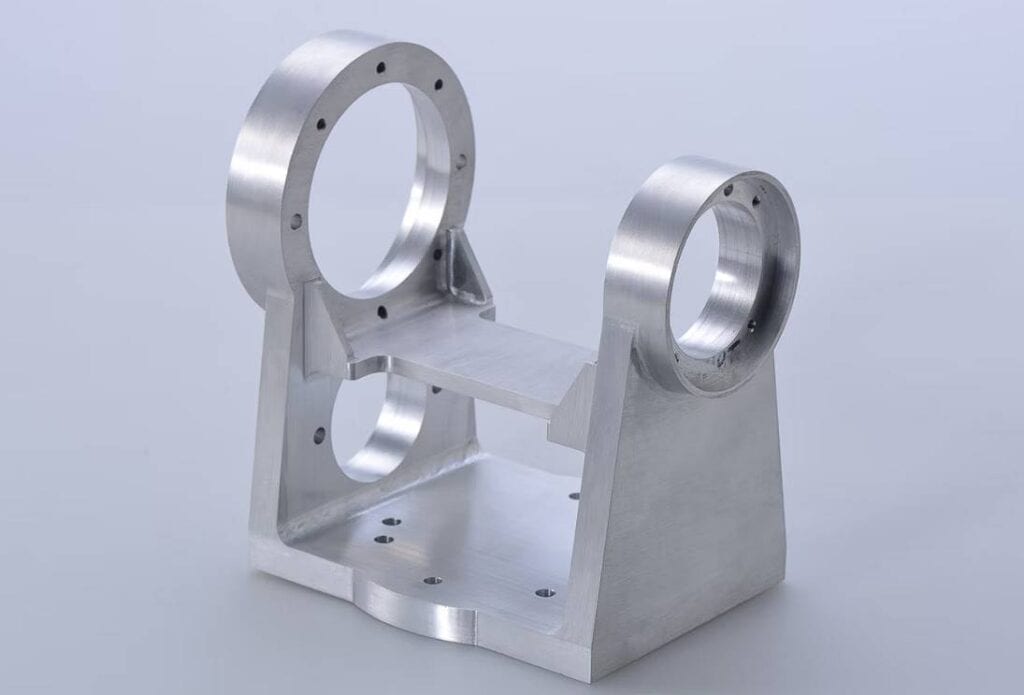
Complex parts can be made with tolerances as fine as 0.004 mm, which is a rather simple process. Not all computer numerical control machines are the same, though. For example, high-precision items can't be made by any CNC machine.
Precision CNC machining is very important in the aerospace and defence industries. The ability to manufacture such exact parts to specifications has the potential to save people's lives.
Endurance
The availability of trained personnel is crucial to the survival of manual machining processes. Production halts every time an employee takes a lunch break or leaves for the day.
A major benefit, however, is that CNC machines can run nonstop, no matter the time of day or year. Depending on the project's specifications, the operator can often programme the machine's computer to produce the appropriate part an unlimited number of times.
Reduced requirement for qualified labourers and engineers makes CNC more cost-effective than traditional machining methods. This allows machine shops to expand their output.
Additionally, CNC machines enable the rapid iteration of the products. If necessary, the operator will adjust the machine's settings to accommodate a small order. After this, the CNC (Computer Numerical Control) programme can be updated for the subsequent manufacturing batch. Because of its versatility, a CNC machine shop can fulfil various requirements, from single prototypes to huge runs of identical parts.
Their low maintenance requirements further enhance CNC machines' durability. With IoT sensors, CNC machines may soon be able to monitor the wear of individual components. The sensors alert the user whenever any wear is noticed. This frees the operator from waiting for the equipment to malfunction before taking corrective action.
Thanks to the IoT, CNC machines can communicate with other devices, such as robots. As a result, the finished product might be removed and packaged without human intervention.
Scalability And High Production
The production process can begin once the operator has entered the required design specifications into the machine's programming. It takes little time for the CNC machine to crank out finished parts once manufacturing begins.
Modern CNC machines can produce many parts and are also highly scalable. Unlike traditional equipment and manual manufacturing procedures, CNC machines are unique because they can be programmed to make a single unit or many identical ones. As a result, companies can make as many components as they need without worrying about running out of money or resources.
Speed
Faster production times are just one of the many benefits of CNC machining. When computer numerical control (CNC) equipment is employed, the fastest speeds allow for significantly increased productivity. All day, every day, CNC machines won't tyre. They can work through the day without stopping for food. No time off or vacation planning is required. With a CNC machine, you won't have to make any sacrifices.
These advantages, along with CNC machining and milling's capacity to maintain a high degree of accuracy and minimise wastage of material resources, make it one of the best ways to guarantee efficient, rapid, and scalable production at a lower cost liability.
When using traditional milling techniques, an operator must physically control the machine and swap out cutting tools as needed. As a result, the process might be quite tedious and ineffective.
Strengthened Abilities
The standard CNC machine features a carousel that can hold up to 30 tools. Automatic tool changes during milling and machining are possible with this setup.
Complex forms can be milled with CNC milling machines using advanced design software.
Regarding productivity, CNC machines are far superior to even the most experienced engineer. Any desired shape, texture, or size can be manufactured using a CNC machine, provided the appropriate software is used.
Capable Of Creating The Most Complex Parts
CNC machining allows for the production of nearly any part imaginable. Shearing, punching holes, flame cutting, and fusing metal sheets are some of the many fabrication and CNC milling processes these machines may carry out.
CNC machines can produce extremely complicated shapes due to their high level of accuracy.
Wide Variety Of Materials
Composites, carving foam, metals, phenolic materials, plastics and rigid foam are just some of the many materials that can be cut successfully by a CNC machine.
Considerations including design tolerance, hardness, fastening, heat tolerance, and stress resistance are important when selecting materials for CNC milling.
Reduced Reliance On Manual Labour And The Potential For Human Error.
CNC lathes and mills are computer-controlled, high-precision turning machinery. Since no human interaction is needed, mistakes caused by humans are eliminated.
CNC machines are controlled by complicated software algorithms that allow them to produce faultless versions of intricate designs.
Design Retention And Uniform Product
The input remains unchanged no matter how often the production cycle is repeated. Likewise, the outputs are consistent unless alterations are made on purpose.
Prototype Digital Simulations
CNC milling and turning are useful for making virtual prototypes. Manufacturers can verify the software's functionality before committing to it for regular use.
Lessen Expenses
Although CNC machines can be pricey up front, they ultimately save businesses money in the long run. CNC machining is cost-effective because of its high output rate, low error rate, and cheap manufacturing costs. Another money saver is the reduced need for training. Learning to operate CNC machines can also be done digitally, saving money and time on training materials. Due to these merits, CNC machining is highly desirable.

Greater Security
An operator's only involvement with a CNC machine is during the programming and upkeep processes. Except for that, it's a fully automated procedure. In addition, workers are less likely to be injured because they won't be as close to the blades during operation.
Fewer incidents related to worker health and safety have occurred since CNC machines were introduced to the manufacturing sector. A computer numerical control machine (CNC) may not be as user-friendly as a cordless drill, but anyone with little training and practice can master it.
Simple Maintenance
The low maintenance requirements of CNC milling machine technology are the cherry on top of a cake of benefits. The service consists primarily of light cleaning and the periodic replacement of cutting tools at specified intervals. As a result, CNC machines require little in the way of upkeep and may often be serviced without the assistance of costly professionals.
The Cnc Industry Is Going To Experience Full Mobility.
A fully portable CNC machine will soon be a reality, much like the widespread availability of the internet.
You can use a desktop CNC machine at home for metal, plastic, and wood cutting. In addition, CNC machines allow factories to automate processes for more difficult projects fully.
Conclusion
CNC machining is a form of metal manufacture in which the CNC machinery is controlled using computer code. It involves removing rather than adding material throughout the making process and employs a block of material (called a blank) and fast-moving cutters to quickly carve away excess material. CNC machines are operated by a digital computer that monitors, automates, and controls the motion of an industrial machine. Different CNC machines include CNC milling, CNC lathes, CNC plasma-cutting machines, and laser-cutting machines. CNC machines are used to produce high-precision parts for industries such as aerospace, automotive, medicine, and electronics.
CNC machines are a subset of computer numerical control machines (CNC machines) that use electrical sparks to shape materials. They use different software programmes, equipment, and machine tools to create the desired shape or design. Software categories for CNC machining include CAM, CAE, and CAD. CAM software extracts technical data from a CAD model, drives the CNC machine, and manipulates the tools to manufacture a unique item. CAE software is used to plan, execute, and debug a project.
CAD software is used to create a virtual prototype of a product, test its functionality, analyse and verify the design of individual components, and share design data with factories and shops. CNC machining is a major advantage over hand-operated methods due to its precision and high precision. It eliminates the potential for human mistakes in part fabrication by following precise computer-generated programming, but the operator still has some say in production. CNC machines can run nonstop, no matter the time of day or year, making them more cost-effective than traditional machining methods. Additionally, CNC machines enable rapid iteration of products, and their low maintenance requirements further enhance their durability.
With IoT sensors, CNC machines may be able to monitor the wear of individual components, freeing the operator from waiting for the equipment to malfunction before taking corrective action. Scalability and high production are also benefits of CNC machines. CNC machines are unique in that they can be programmed to make a single unit or many identical ones, allowing companies to make as many components as they need without running out of money or resources. They have faster production times, stronger abilities, and the capacity to maintain a high degree of accuracy and minimise wastage of material resources, making them one of the best ways to guarantee efficient, rapid, and scalable production at a lower cost liability. They can also create the most complex parts due to their high level of accuracy.
Materials such as composites, carving foam, metals, phenolic materials, plastics and rigid foam can be cut successfully by CNC machines. CNC lathes and mills are computer-controlled, high-precision turning machinery that eliminates reliance on manual labour and the potential for human error. They are also cost-effective due to their high output rate, low error rate, and cheap manufacturing costs. Additionally, they are user-friendly and require little maintenance. The CNC industry is going to experience full mobility, allowing factories to automate processes for more difficult projects fully.
Content Summary
- CNC machining has radically altered precision manufacturing.
- CNC machining is indispensable in producing high-precision parts for various industries.
- CNC machining involves subtractive manufacturing, removing material to create the final product.
- It is different from additive manufacturing, which uses 3D printers to add layers of material.
- CNC machines are controlled by computer code.
- CNC milling is a popular form of CNC machining known for its precision and tight tolerances.
- CNC turning involves the material being turned to remove it.
- CNC plasma cutting machines use a plasma torch to cut strong materials like metal.
- CNC laser cutting machines employ a laser beam for cutting materials with high precision.
- CNC electric discharge machines use electrical sparks to shape materials.
- CNC machining uses different software programs like CAM, CAE, and CAD.
- CAM software extracts technical data from a CAD model to drive the CNC machine.
- CAE software is used for engineering analysis and project planning.
- CAD software is used for designing and creating technical drawings in 2D or 3D.
- CNC machines offer improved accuracy and high precision.
- CNC machines can operate continuously without the need for breaks or vacations.
- CNC machines reduce the requirement for qualified labourers and engineers.
- CNC machines require low maintenance and can monitor wear using IoT sensors.
- CNC machines can communicate with other devices like robots for automated processes.
- CNC machining allows for rapid production and scalability.
- CNC machines operate at faster speeds, increasing productivity.
- CNC machines can produce complex forms and shapes with advanced design software.
- CNC machining can create nearly any part imaginable using various fabrication processes.
- CNC machines can cut a wide variety of materials, including composites and metals.
- CNC machines eliminate human errors and reliance on manual labour.
- CNC machines provide design retention and uniformity in production.
- CNC machining can be used for virtual prototypes and software verification.
- CNC machining is cost-effective in the long run, with high output and low error rates.
- CNC machines offer greater security with automated processes and reduced worker incidents.
- CNC machines require simple maintenance and can be serviced without expensive professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions
CNC machining is highly precise, with typical tolerances ranging from +/- 0.005 to 0.001 inches (0.127 to 0.0254 mm). However, the achievable precision depends on various factors, including machine capabilities, tooling, and the project's specific requirements.
Yes, CNC machining is often used for rapid prototyping. It allows for the quick production of functional prototypes, enabling designers and engineers to validate their designs before moving to mass production.
The cost of CNC machining depends on various factors, such as the part's complexity, material selection, machine setup time, and quantity needed. While CNC machining can be more expensive than some other manufacturing methods for small production runs, it becomes cost-effective for larger quantities or when precision and quality are essential.
CNC machining has some limitations, such as difficulties in creating internal corners with sharp radii, limitations on the size of parts that can be produced, and the need for skilled operators to program and operate the machines.
While CNC machines and 3D printers share similarities in terms of computer-controlled automation, they are different technologies. CNC machines remove material to create a part, while 3D printers add material layer by layer. However, hybrid machines combine CNC machining and 3D printing capabilities, offering the advantages of both technologies in a single system.